graph_tool.centrality.hits#
- graph_tool.centrality.hits(g, weight=None, xprop=None, yprop=None, epsilon=1e-06, max_iter=None)[source]#
Calculate the authority and hub centralities of each vertex in the graph.
- Parameters:
- g
Graph Graph to be used.
- weight
EdgePropertyMap(optional, default:None) Edge property map with the edge weights.
- xprop
VertexPropertyMap, optional (default:None) Vertex property map where the authority centrality must be stored.
- yprop
VertexPropertyMap, optional (default:None) Vertex property map where the hub centrality must be stored.
- epsilonfloat, optional (default:
1e-6) Convergence condition. The iteration will stop if the total delta of all vertices are below this value.
- max_iterint, optional (default:
None) If supplied, this will limit the total number of iterations.
- g
- Returns:
- eigfloat
The largest eigenvalue of the cocitation matrix.
- x
VertexPropertyMap A vertex property map containing the authority centrality values.
- y
VertexPropertyMap A vertex property map containing the hub centrality values.
See also
betweennessbetweenness centrality
eigenvectoreigenvector centrality
pagerankPageRank centrality
trust_transitivitypervasive trust transitivity
Notes
The Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search (HITS) centrality assigns hub (\(\mathbf{y}\)) and authority (\(\mathbf{x}\)) centralities to the vertices, following:
\[\begin{split}\begin{align} \mathbf{x} &= \alpha\mathbf{A}\mathbf{y} \\ \mathbf{y} &= \beta\mathbf{A}^T\mathbf{x} \end{align}\end{split}\]where \(\mathbf{A}\) is the (weighted) adjacency matrix and \(\lambda = 1/(\alpha\beta)\) is the largest eigenvalue of the cocitation matrix, \(\mathbf{A}\mathbf{A}^T\). (Without loss of generality, we set \(\beta=1\) in the algorithm.)
The algorithm uses the power method which has a topology-dependent complexity of \(O\left(N\times\frac{-\log\epsilon}{\log|\lambda_1/\lambda_2|}\right)\), where \(N\) is the number of vertices, \(\epsilon\) is the
epsilonparameter, and \(\lambda_1\) and \(\lambda_2\) are the largest and second largest eigenvalues of the (weighted) cocitation matrix, respectively.If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
[hits-algorithm][kleinberg-authoritative]J. Kleinberg, “Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment”, Journal of the ACM 46 (5): 604-632, 1999, DOI: 10.1145/324133.324140 [sci-hub, @tor].
[power-method][adamic-polblogs] (1,2)L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 [sci-hub, @tor]
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"] >>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g)) >>> ee, x, y = gt.hits(g) >>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=x, ... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(x, mi=5, ma=15), ... vcmap=matplotlib.cm.gist_heat, ... vorder=x, output="polblogs_hits_auths.pdf") <...> >>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=y, ... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(y, mi=5, ma=15), ... vcmap=matplotlib.cm.gist_heat, ... vorder=y, output="polblogs_hits_hubs.pdf") <...>
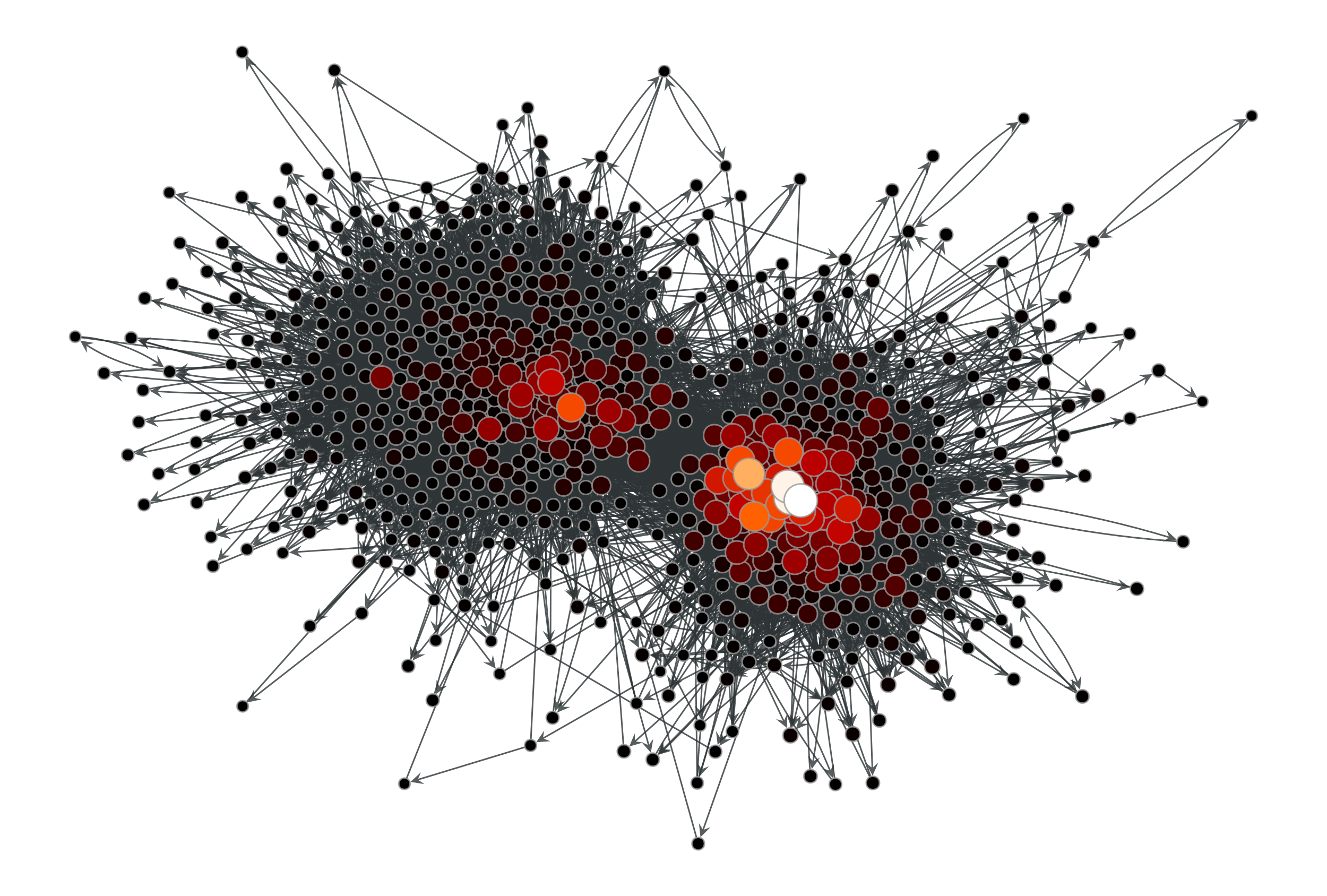
HITS authority values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].#
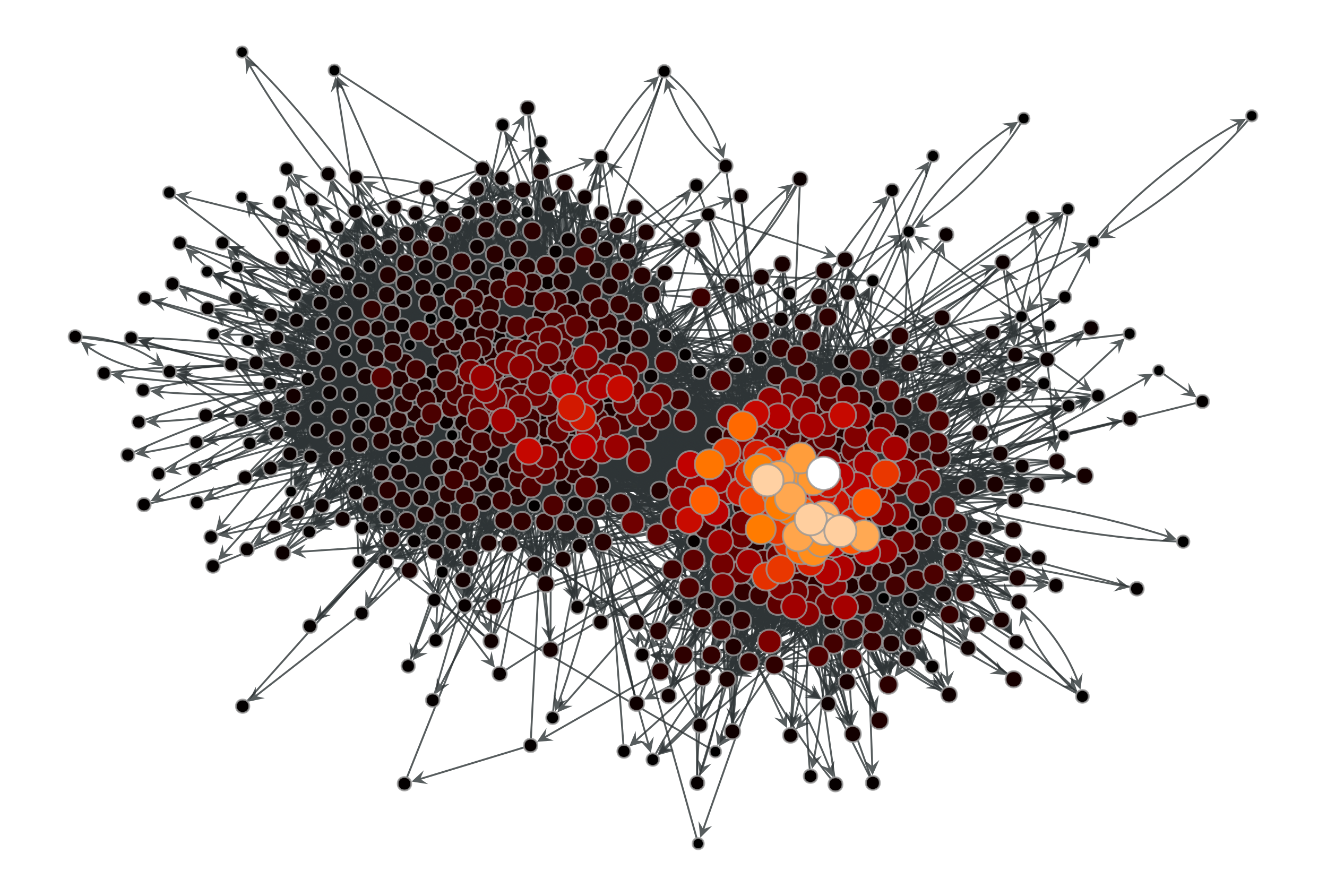
HITS hub values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].#