graph_tool.centrality.pagerank#
- graph_tool.centrality.pagerank(g, damping=0.85, pers=None, weight=None, prop=None, epsilon=1e-06, max_iter=None, ret_iter=False)[source]#
Calculate the PageRank of each vertex.
- Parameters:
- g
Graph Graph to be used.
- dampingfloat, optional (default: 0.85)
Damping factor.
- pers
VertexPropertyMap, optional (default: None) Personalization vector. If omitted, a constant value of \(1/N\) will be used.
- weight
EdgePropertyMap, optional (default: None) Edge weights. If omitted, a constant value of 1 will be used.
- prop
VertexPropertyMap, optional (default: None) Vertex property map to store the PageRank values. If supplied, it will be used uninitialized.
- epsilonfloat, optional (default: 1e-6)
Convergence condition. The iteration will stop if the total delta of all vertices are below this value.
- max_iterint, optional (default: None)
If supplied, this will limit the total number of iterations.
- ret_iterbool, optional (default: False)
If true, the total number of iterations is also returned.
- g
- Returns:
- pagerank
VertexPropertyMap A vertex property map containing the PageRank values.
- pagerank
See also
betweennessbetweenness centrality
eigentrusteigentrust centrality
eigenvectoreigenvector centrality
hitsauthority and hub centralities
trust_transitivitypervasive trust transitivity
Notes
The value of PageRank [pagerank-wikipedia] of vertex v, \(PR(v)\), is given iteratively by the relation:
\[PR(v) = \frac{1-d}{N} + d \sum_{u \in \Gamma^{-}(v)} \frac{PR (u)}{d^{+}(u)}\]where \(\Gamma^{-}(v)\) are the in-neighbors of v, \(d^{+}(u)\) is the out-degree of u, and d is a damping factor.
If a personalization property \(p(v)\) is given, the definition becomes:
\[PR(v) = (1-d)p(v) + d \sum_{u \in \Gamma^{-}(v)} \frac{PR (u)}{d^{+}(u)}\]If edge weights are also given, the equation is then generalized to:
\[PR(v) = (1-d)p(v) + d \sum_{u \in \Gamma^{-}(v)} \frac{PR (u) w_{u\to v}}{d^{+}(u)}\]where \(d^{+}(u)=\sum_{y}A_{u,y}w_{u\to y}\) is redefined to be the sum of the weights of the out-going edges from u.
If a node has out-degree zero, it is assumed to connect to every other node with a weight proportional to \(p(v)\) or a constant if no personalization is given.
The implemented algorithm progressively iterates the above equations, until it no longer changes, according to the parameter epsilon. It has a topology-dependent running time.
If enabled during compilation, this algorithm runs in parallel.
References
[lawrence-pagerank-1998]P. Lawrence, B. Sergey, M. Rajeev, W. Terry, “The pagerank citation ranking: Bringing order to the web”, Technical report, Stanford University, 1998
[Langville-survey-2005]A. N. Langville, C. D. Meyer, “A Survey of Eigenvector Methods for Web Information Retrieval”, SIAM Review, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 135-161, 2005, DOI: 10.1137/S0036144503424786 [sci-hub, @tor]
[adamic-polblogs] (1,2)L. A. Adamic and N. Glance, “The political blogosphere and the 2004 US Election”, in Proceedings of the WWW-2005 Workshop on the Weblogging Ecosystem (2005). DOI: 10.1145/1134271.1134277 [sci-hub, @tor]
Examples
>>> g = gt.collection.data["polblogs"] >>> g = gt.GraphView(g, vfilt=gt.label_largest_component(g)) >>> pr = gt.pagerank(g) >>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=pr, ... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(pr, mi=5, ma=15), ... vorder=pr, vcmap=matplotlib.cm.gist_heat, ... output="polblogs_pr.pdf") <...>

PageRank values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs].#
Now with a personalization vector, and edge weights:
>>> d = g.degree_property_map("total") >>> periphery = d.a <= 2 >>> p = g.new_vertex_property("double") >>> p.a[periphery] = 100 >>> pr = gt.pagerank(g, pers=p) >>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=g.vp["pos"], vertex_fill_color=pr, ... vertex_size=gt.prop_to_size(pr, mi=5, ma=15), ... vorder=pr, vcmap=matplotlib.cm.gist_heat, ... output="polblogs_pr_pers.pdf") <...>
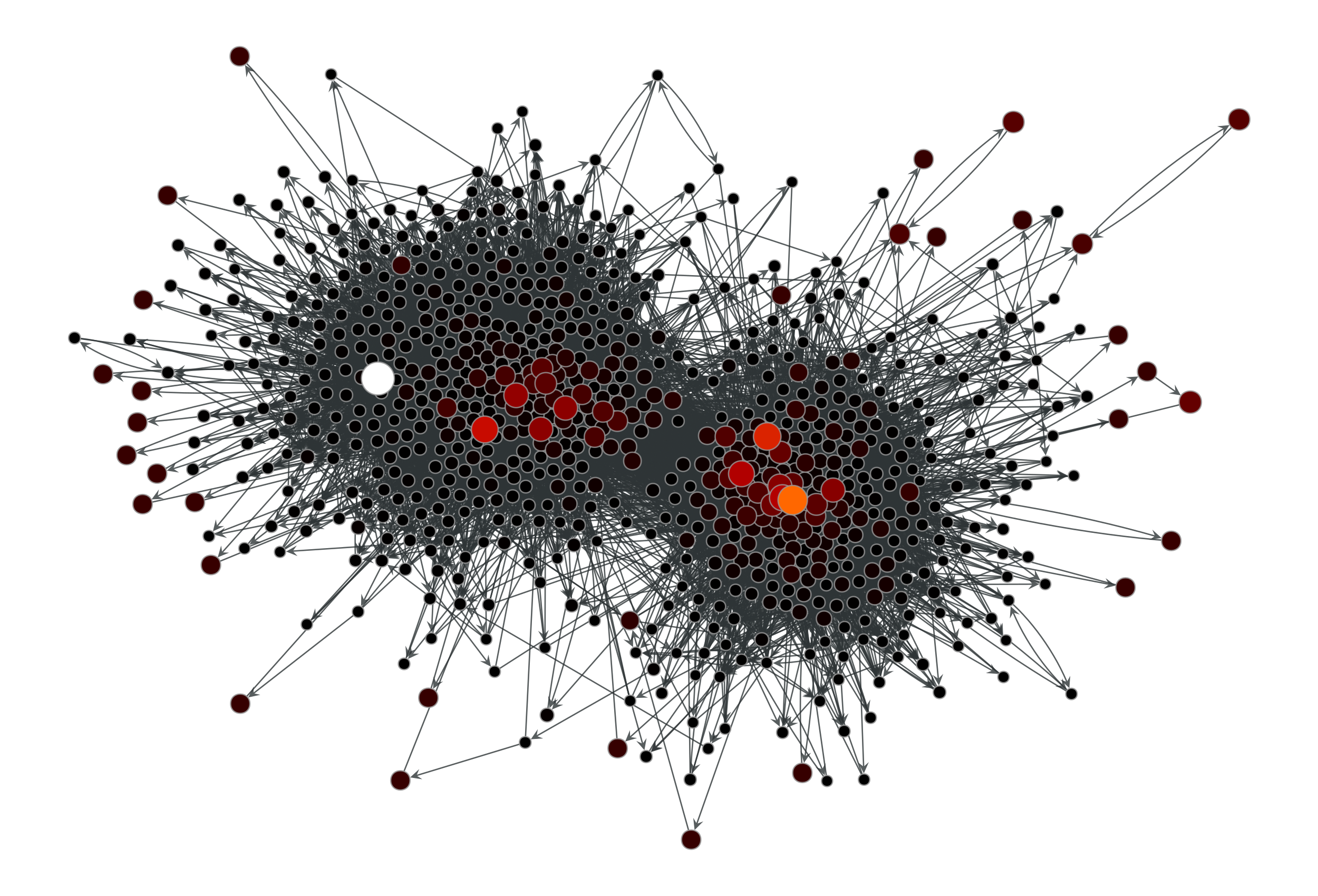
Personalized PageRank values of the a political blogs network of [adamic-polblogs], where vertices with very low degree are given artificially high scores.#