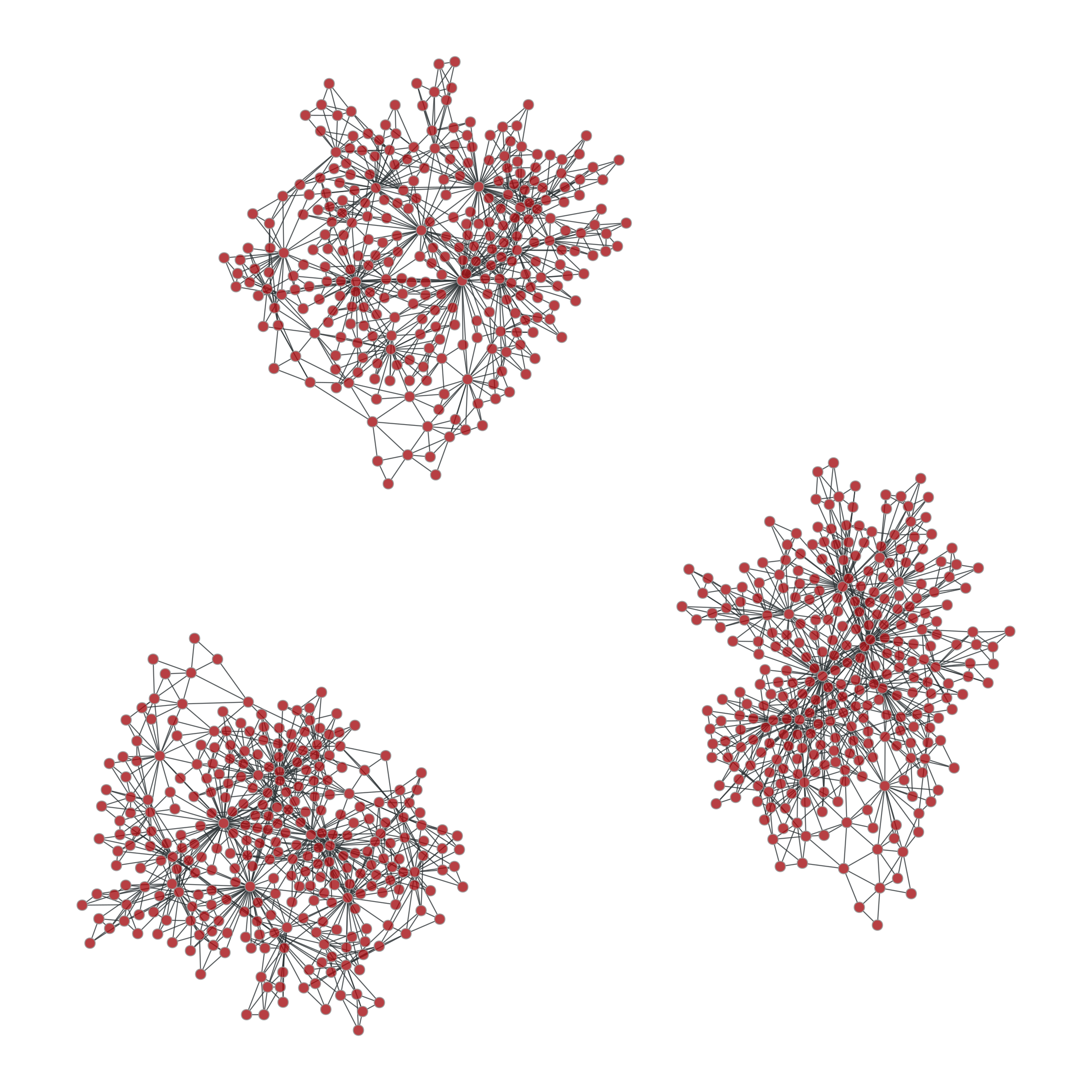graph_tool.generation.graph_union#
- graph_tool.generation.graph_union(g1, g2, intersection=None, props=None, include=False, internal_props=False)[source]#
Return the union of graphs
g1andg2, composed of all edges and vertices ofg1andg2, without overlap (ifintersection == None).- Parameters:
- g1
Graph First graph in the union.
- g2
Graph Second graph in the union.
- intersection
VertexPropertyMap(optional, default:None) Vertex property map owned by g2 which maps each of its vertices to vertex indices belonging to g1. Negative values mean no mapping exists, and thus both vertices in g1 and g2 will be present in the union graph.
- propslist of tuples of
PropertyMap(optional, default:None) Each element in this list must be a tuple of two PropertyMap objects. The first element must be a property of g1, and the second of g2. If either value is
None, an empty map is created. The values of the property maps are propagated into the union graph, and returned.- includebool (optional, default:
False) If
True, graph g2 is inserted in-place into g1, which is modified. IfFalse, a new graph is created, and both graphs remain unmodified.- internal_propsbool (optional, default:
False) If
True, all internal property maps are propagated, in addition toprops.
- g1
- Returns:
- ug
Graph The union graph
- propslist of
PropertyMapobjects List of propagated properties. This is only returned if props is not empty.
- ug
Examples
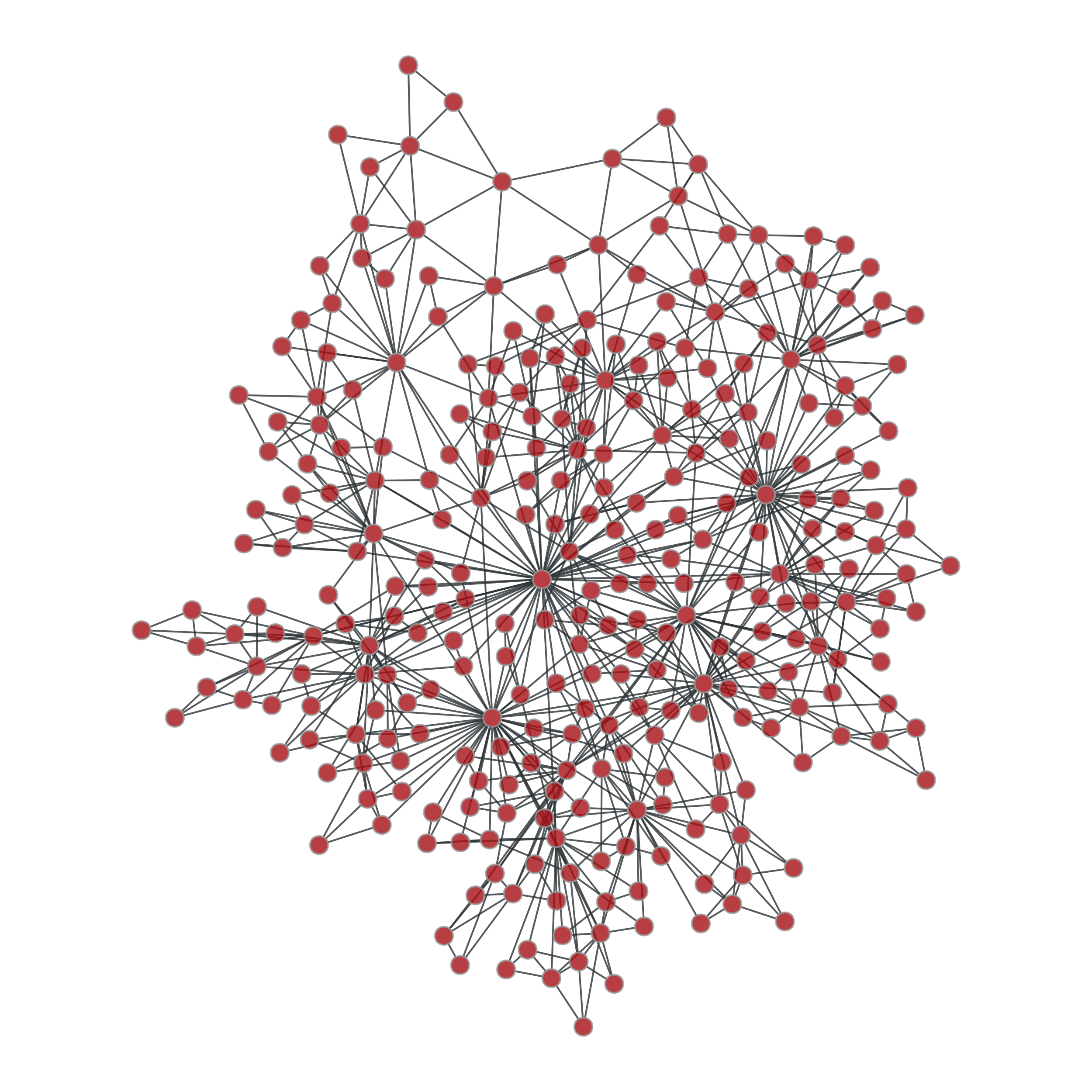
>>> g = gt.triangulation(random((300,2)))[0] >>> ug = gt.graph_union(g, g) >>> uug = gt.graph_union(g, ug) >>> pos = gt.sfdp_layout(g) >>> gt.graph_draw(g, pos=pos, adjust_aspect=False, output="graph_original.pdf") <...>
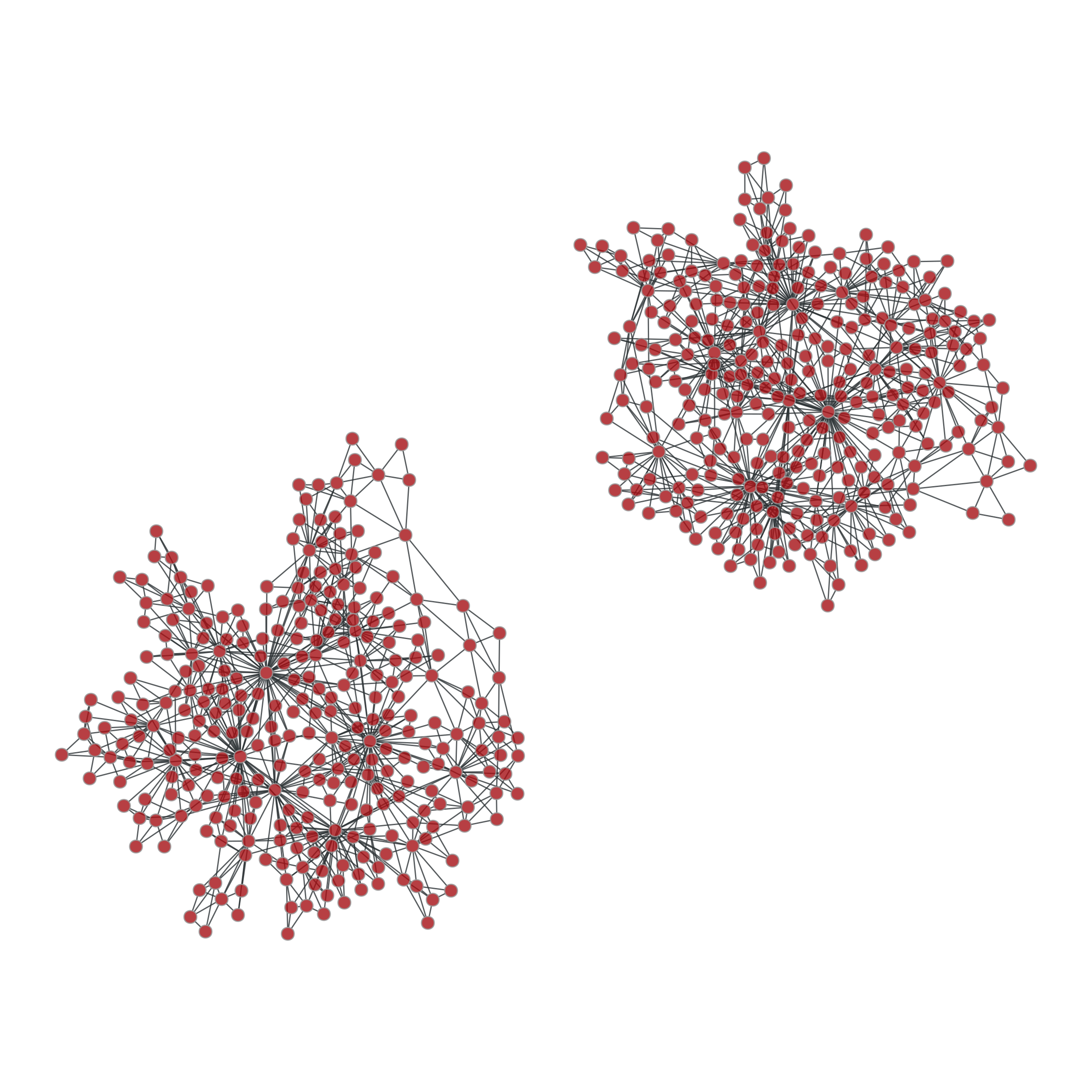
>>> pos = gt.sfdp_layout(ug) >>> gt.graph_draw(ug, pos=pos, adjust_aspect=False, output="graph_union.pdf") <...>
>>> pos = gt.sfdp_layout(uug) >>> gt.graph_draw(uug, pos=pos, adjust_aspect=False, output="graph_union2.pdf") <...>